What Is Disc Disease?
Symptomatic disc disease is most often identified by pain in the cervical (neck) or lumbar (low back) spine with pain, numbness and tingling in the corresponding upper or lower extremities. Severe back pain with bending forward can also indicate painful disc disease called discogenic pain.
As we age, discs in the Cervical, Thoracic and Lumbar spine can lose some of their fluid, and become dessicated or dried out. When the disc becomes compressed it can put pressure on the outer ring, called the annulus causing a disc bulge. A disc bulge, much like a bulging tire, is where the disc wall is intact but is weak and protruding.
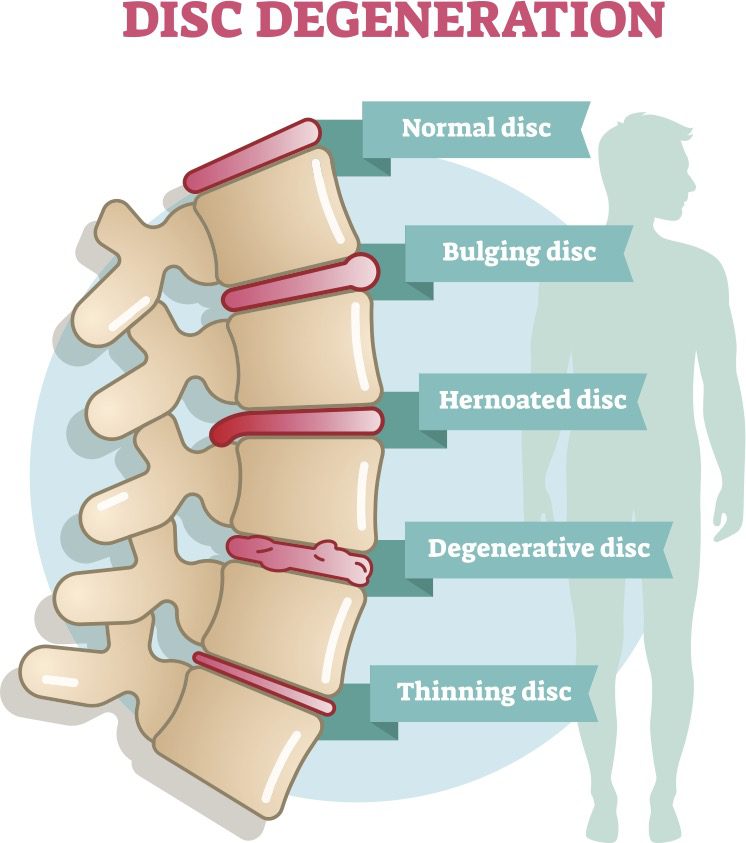
Disc Herniation is where the disc wall ruptures and the gel-like nucleus partially leaks out, and can occur as a result of excessive load or pressure on the discs. A disc herniation can cause issues and severe pain by pushing on or compressing the nerve roots most often in the cervical and lumbar spine.
A Quick Anatomy Lesson
The spinal column also known as the backbone is made up of multiple bones called vertebrae. The vertebrae in the spinal column are separated into section by region, the neck also known as the cervical spine and is made up of 7 vertebrae, the mid back or the Thoracic spine is made up of 12 vertebrae, and the low back also known as the Lumbar spine is made up of 5 vertebrae.
What are Discs and Why Are They So Important?
Between each of the vertebrae in the spine are the discs, these spongy pillow-like structures have a fibrous outer coating like the tread on a tire and a gel in the middle instead of air. The discs are important structures that offer shock absorption in the lumbar spine by distributing compressive loads placed on the spine while providing motion for the spine.

How is the Condition Diagnosed?
Disc disease of the spine is usually diagnosed incidentally by Xray or MRI of the cervical, thoracic or lumbar spine. These studies are usually ordered when there is pain in the lumbar spine to rule out disc herniation or other pathology. MRI shows soft tissue structures and can identify if a disk is compressing surrounding nerve roots or narrowing the central spinal canal.
How can Disc Disease be Treated?
The severity of disc disease and the number of discs involved varies with age. There are many treatments depending on the signs and symptoms that can reduce pain and improve function. For cervical and lumbar disc bulges and herniations that cause radicular or extremity symptoms, treatment options include epidural steroid injections where anti-inflammatory steroids are injected around the disc and nerve roots surrounding to reduce inflammation and pain.
How Can I Combat Lumbar Disc Disease and Maintain an Active Lifestyle?
Low impact weight bearing exercise with core muscle strengthening on a regular basis has been shown very effective in reducing pain and improving function. Weight bearing exercise is an important part of maintaining bone density as well. Examples are dancing, high impact aerobics, hiking, jogging/running, jumping rope, stair climbing/elliptical, tennis.
Supplements including Vitamin D3 that support bone and cartilage health are an important part of maintaining a healthy spine. Fish oil can be helpful in combating inflammation in the body which can accelerate arthritis and disc degeneration.
Regenerative Medicine techniques such as Platelet Rich Plasma and Bone Marrow Aspirate Concentrate (Stem Cell Therapy) can be used and have proven to be quite effective. Stem cell therapy is done by injecting a person’s own stem cells from bone marrow into the disc to strengthen the disc wall. Platelet rich plasma can also be used to treat other structures in the spine that become degenerative.

Michelle Hall
PA-CPhysician Assistant




