Recently I have been noticing some occasional inflammation in some joints in my hands intermittently. I eat reasonably healthy and try to exercise on a regular basis. I began to think about inflammation and really relate to many of my patients young and old that ask me about the subject. With my personal interest peaked I decided to delve into the subject once again and share the information and pearls with all of you in hopes that it can be useful to all of us.
Inflammation: What is it?
Inflammation is our body’s natural response to damaged tissues in the body that can be caused by many things including trauma, heat injury and toxins just to name a few. When the body senses that there is an injury to tissue, this sets off a whole chain reaction. Signaling molecules send out messages that start the healing process where blood flow is increased to the area, white blood cells are recruited to fight off invading bacteria and platelets are recruited to begin the healing process.
Acute vs. Chronic Inflammation
Before we go any further we need to talk about the two types of inflammation, acute and chronic. Acute inflammation occurs when there is a new injury and the process of healing begins. Chronic inflammation occurs when the agent that causes the inflammation persists in the tissues and then starts to release proinflammatory factors that encourage more inflammation in the area resulting in more damage to localized structures. This self perpetuating negative cascade of events can lead to chronic inflammatory disease states including Rheumatoid Arthritis, Crohn’s Disease, Joint disease including Osteoarthritis, Heart Disease and Diabetes.
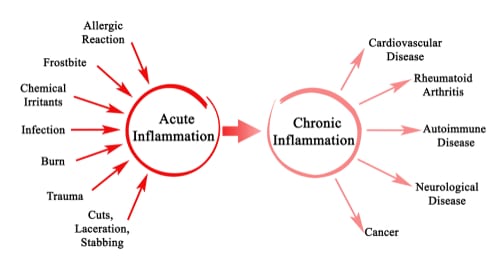
Basically, acute inflammation serves a specific purpose to signal the body when there is an injury to heal itself, but chronic inflammation is unhealthy for the body and can lead to long term consequences.
Key Ways to Reduce Inflammation
Now that we know the importance of reducing prolonged inflammation in the body to live longer healthier lives, the question is how do we go about it?
Diet
As annoying as it is, one of the key ways to reduce inflammation in the body is by eating a healthy diet! So what are the do’s and don’ts?
Don’ts: Foods that Promote Inflammation:
- Fried foods: Studies show that foods high in saturated fats increase inflammatory markers in the body.
- Red Meat and processed meats: I was a bit confused about why red meat can lead to inflammation, but from what I read it seems to be related to the saturated fat content in the meat. Suggestions are made to limit red meat to and when eating it choose lean meat and smaller servings.
- Refined carbohydrates including simple sugars: Examples include white bread, pastries, candy and soda. Foods and drinks that have a high glycemic index i.e. refined sugars make our pancreas work harder to secrete insulin to break down the sugar to be absorbed by cells in the body. Increased sugar leads to increased body weight and obesity has been linked to increased body inflammation.
The Do’s: Foods That Reduce Inflammation:

- Green Leafy Vegetables: Green leafy vegetables are a source of beta carotene and magnesium, both of which in addition to other nutrients have been found to decrease Inflammatory markers in studies.
- Nuts/ Salmon/ Foods rich in Omega 3 Fatty Acids: Studies have shown that eating foods rich in Omega 3 fatty acids reduce inflammatory markers such as CRP. Examples of these foods includes salmon, fatty fish, almonds, walnuts, pecans, cashews.
- Fruits High in Anti Oxidants: Think of blues and reds, this includes blueberries, cherries, strawberries, and oranges.
Exercise
- Studies show that people who engage in daily activity and a regular exercise routine of at least 20 minutes a day have reduced levels of inflammatory markers including C- Reactive Protein.
- Yoga performed on a regular basis either daily or several times a week has been shown in more than one study to reduce multiple inflammatory markers in the body. There is also the additional benefit of reducing stress levels!

Stress Reduction
Increased stress and reactions to stressful situations and emotions can increase body inflammation. Easier said than done to reduce daily stress but here are some suggestions.
- Getting a massage has been shown to both be relaxing and reduce inflammatory markers in the body.
- Yoga which incorporates exercise and breathing techniques is a good way to reduce stress.
- Meditation and mindfulness are ways to reduce stress. There are several apps available for meditation.
Supplements
Last but not least, the subject that I am most asked about are what supplements can be taken to reduce inflammation.
- Magnesium: This often ignored supplement has been shown to lower inflammatory markers and the best part is beneficial to the heart, muscle and many other structures in the body.
- Vitamin D3: A fat loving vitamin best absorbed when taken with a large fatty meal, this supplement is known to help with bone and joint health and lowers inflammatory markers as well. Most people can easily take 5,000 IU of D3 per day.
- Vitamin C: Vitamin C supplementation of 1,000 mg/day decreased inflammatory markers in patients with increased CRP (C Reactive Protein). Vitamin C has been shown to protect heart health as well.
- B Vitamins: B vitamins are helpful in so many ways, they help maintain the body’s neurologic system, and B6 and B12 can be helpful in reducing inflammation.
There are many other supplements that could be helpful I did not list here, but these are some of the big ones.
I found in my research that there are so many ways to reduce inflammation, the most important thing is living a healthy lifestyle!

Michelle Hall
PA-CPhysician Assistant




